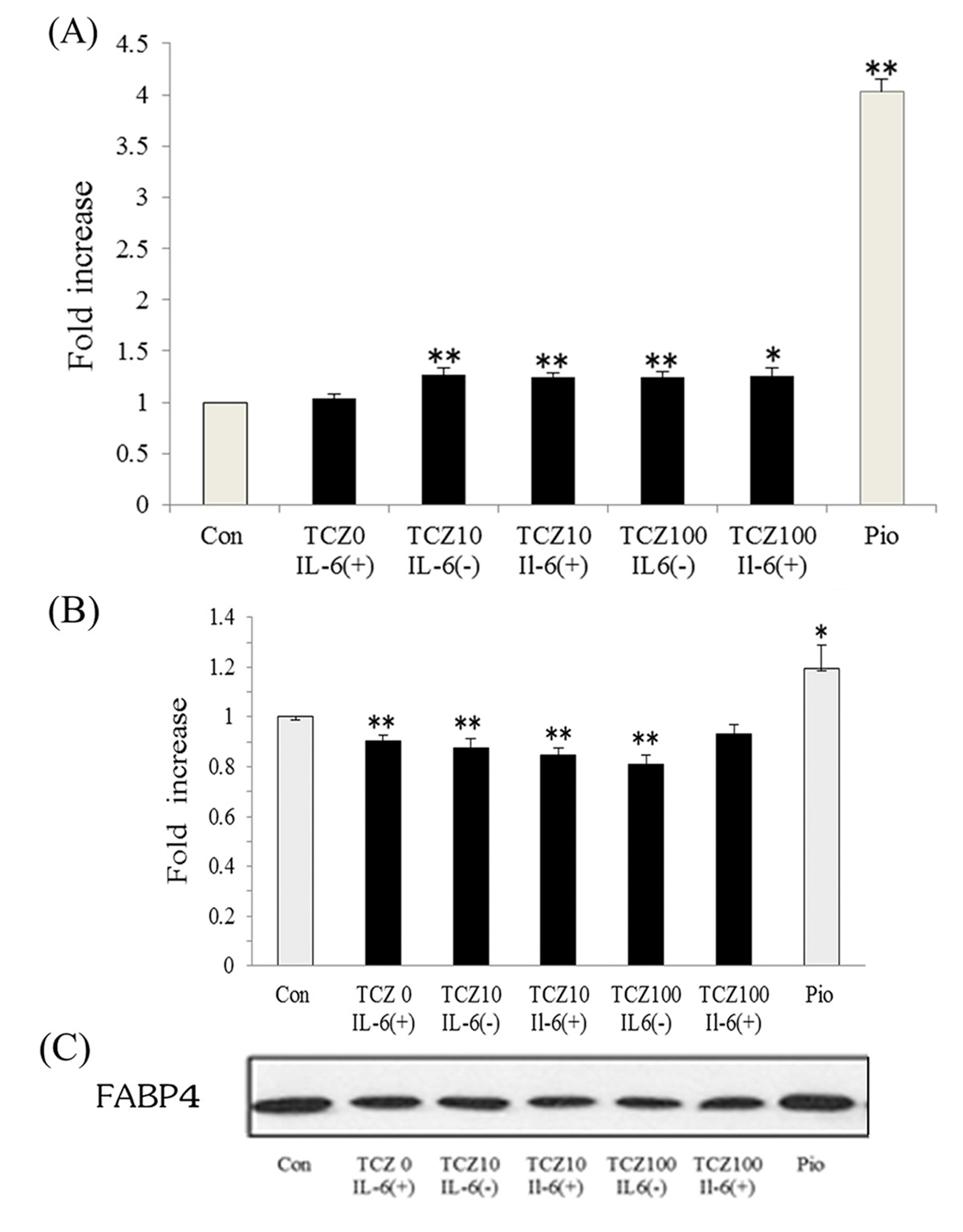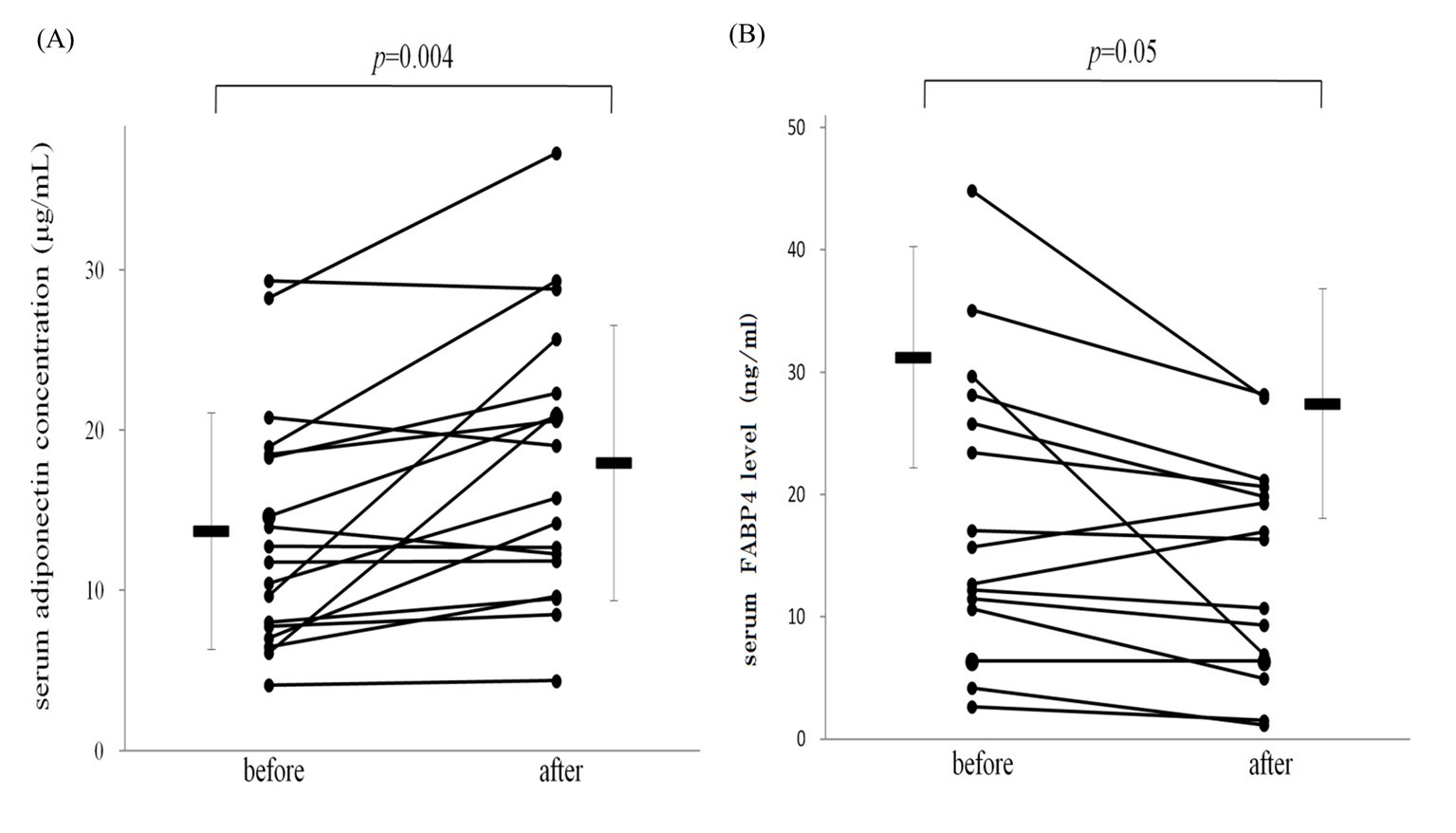
Figure 1. Treatment with tocilizumab increased serum adiponectin (A) and decreased fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels (B) in patients with RA. Bars represent mean ± SEM.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Original Article
Volume 4, Number 5-6, December 2014, pages 143-147
Tocilizumab Increases Serum Adiponectin and Reduces Serum Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Figures