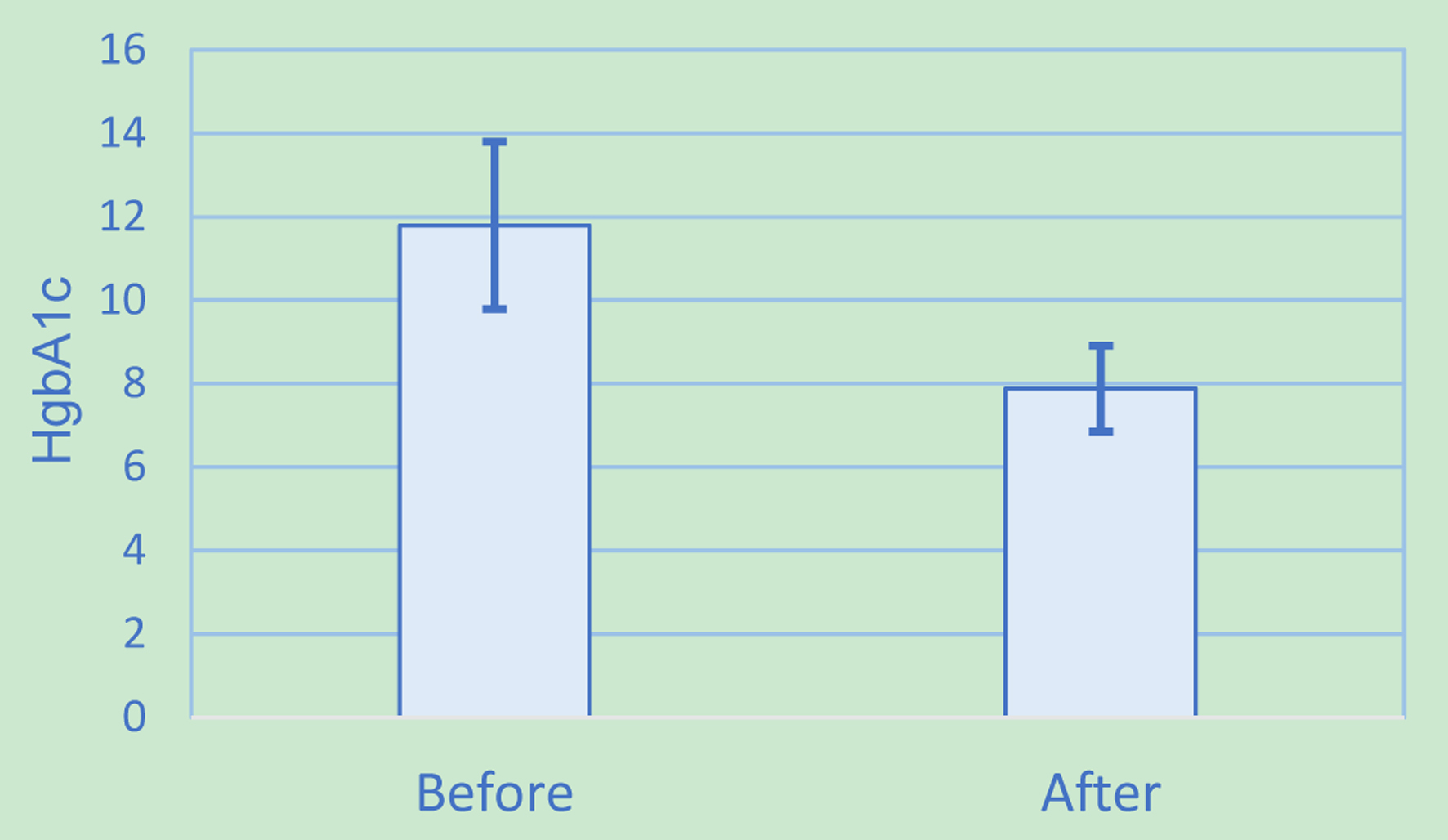
Figure 1. Hemoglobin A1c results.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jofem.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 2, June 2023, pages 70-74
Intensive Management of Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Using a Multidisciplinary Approach and Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Figure

Tables
| BMI: body mass index; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c. | |
| Number of patients | 16 |
| Mean age | 56.9 |
| Gender (% female) | 62.5% |
| Mean BMI | 32.2 |
| Mean initial HbA1c % (mmol/mol) | 11.8 (105) |
| Mean (initial) | SD | Mean (final) | SD | Change | SD | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; BG: blood glucose; TIR: time in range; TAR: time above range; TBR: time below range; BMI: body mass index; SD: standard deviation. | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 11.79 | 2.00 | 7.88 | 1.03 | -3.91 | 1.11 | < 0.001 |
| Average BG (mg/dL) | 185.38 | 48.81 | 172.31 | 36.94 | -13.08 | 28.86 | 0.13 |
| TIR (%) | 52.54 | 28.68 | 60.61 | 22.72 | +8.08 | 16.43 | 0.10 |
| TAR (%) | 46.46 | 29.37 | 38.69 | 23.19 | -7.77 | 17.35 | 0.13 |
| TBR (%) | 1.00 | 1.29 | 0.69 | 1.03 | -0.31 | 1.38 | 0.44 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.20 | 5.83 | 31.65 | 5.68 | -0.55 | 1.53 | 0.17 |