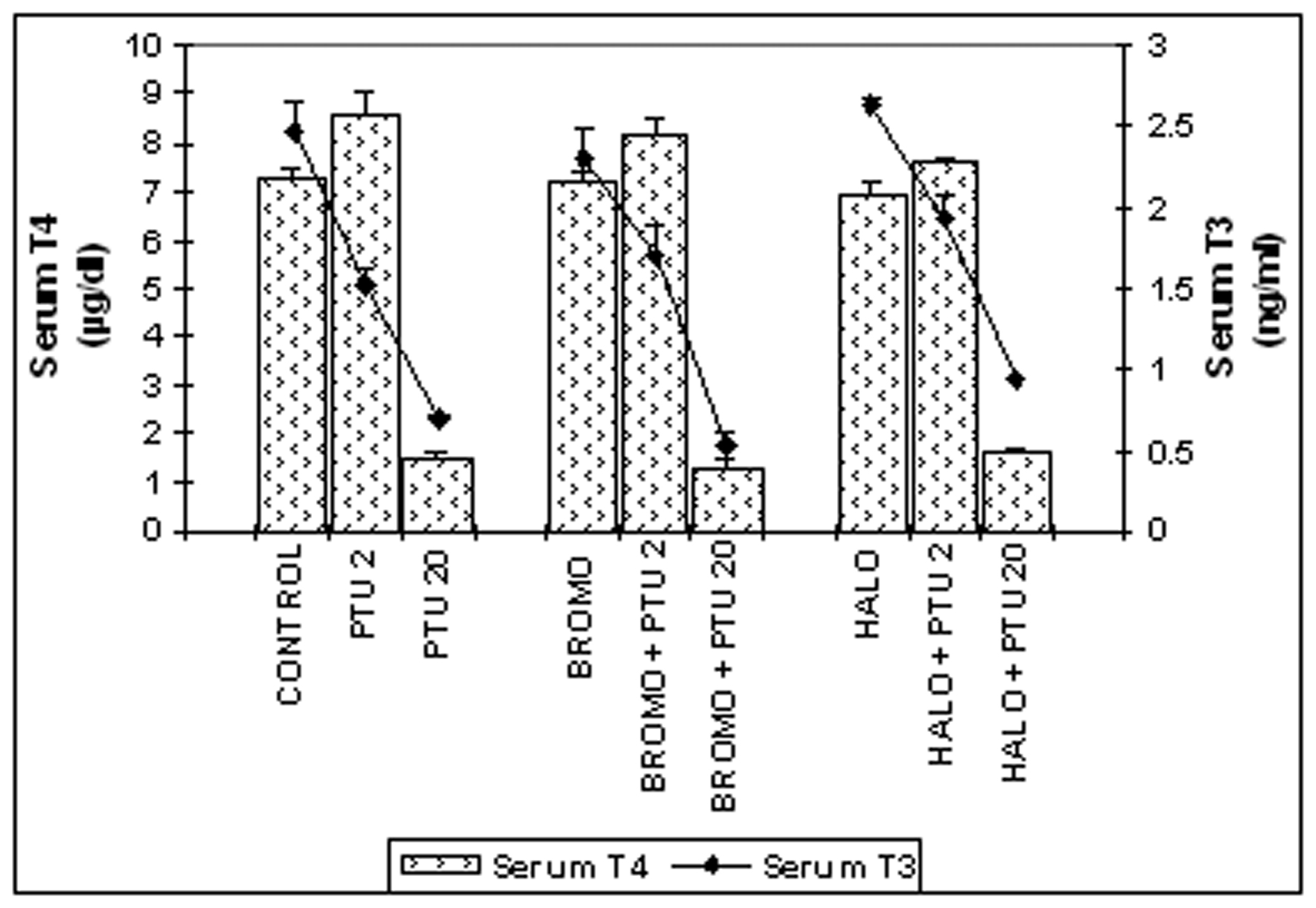
Figure 1. Serum total T4 (mg/dL) and T3 (ng/mL) concentrations. Daily intra-peritoneal injections of different doses of Bromocriptine (BROMO, dopaminergic agonist) and Haloperidol (HALO, antagonist) were given to adult male Sprague Dawley rats either singly or in combination with PTU (2 mg/100g b.w.) for the first (Day ‘0’ and ‘1’) and last (Day ‘18’ and ‘19’) two consecutive days preceding the onset (Day ‘2’) and termination (Day ‘20’), of 'central thyroid hormone homeostasis'. Parallel control animals were injected with equal volume of vehicle. Blood samples for T4/T3 ELISA were collected from the retro-orbital sinus on the day of onset (Day ‘2’) and termination (Day ‘20’) of ‘central homeostasis’ and 24 h after the last injections. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM of 12 - 15 individuals in each group, pooled from three sets of experiments. The vertical lines denote standard error.
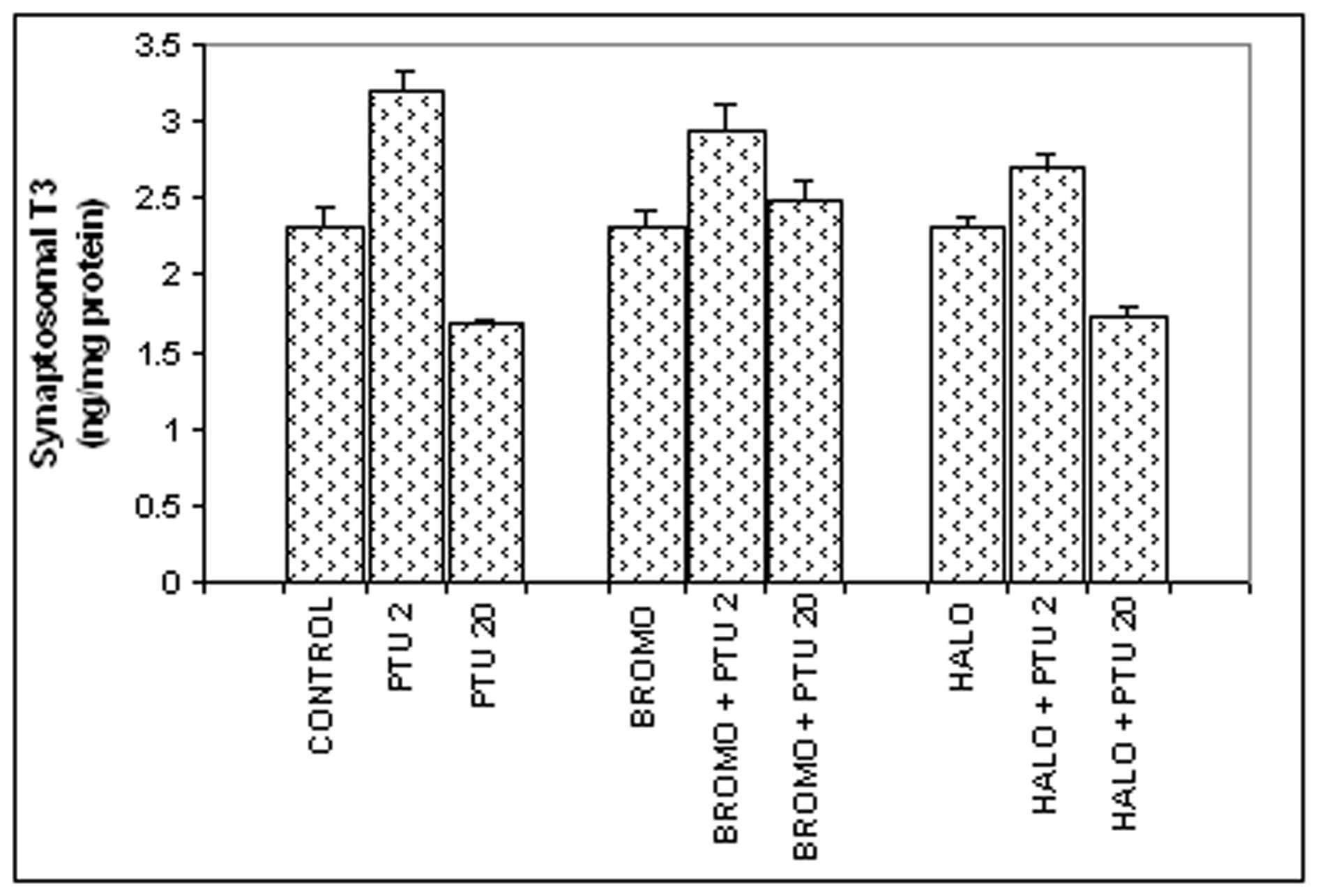
Figure 2. Synaptosomal total T3 content (ng/mg synaptosomal protein). Daily intra-peritoneal injections of different doses of Bromocriptine (BROMO, dopaminergic agonist) and Haloperidol (HALO, antagonist) were given to adult male Sprague Dawley rats either singly or in combination with PTU (2 mg/100g b.w.) for the first (Day ‘0’ and ‘1’) and last (Day ‘18’ and ‘19’) two consecutive days preceding the onset (Day ‘2’) and termination (Day ‘20’), respectively, of 'central thyroid hormone homeostasis'. Parallel control animals were injected with equal volume of vehicle. Animals were sacrificed and cerebral cortex collected on Day ‘2’ and Day ‘20’ (after 24 h of the last injections) for preparation of synaptosome for T3 ELISA. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM of 12 - 15 individuals in each group, pooled from three sets of experiments. The vertical lines denote standard error.
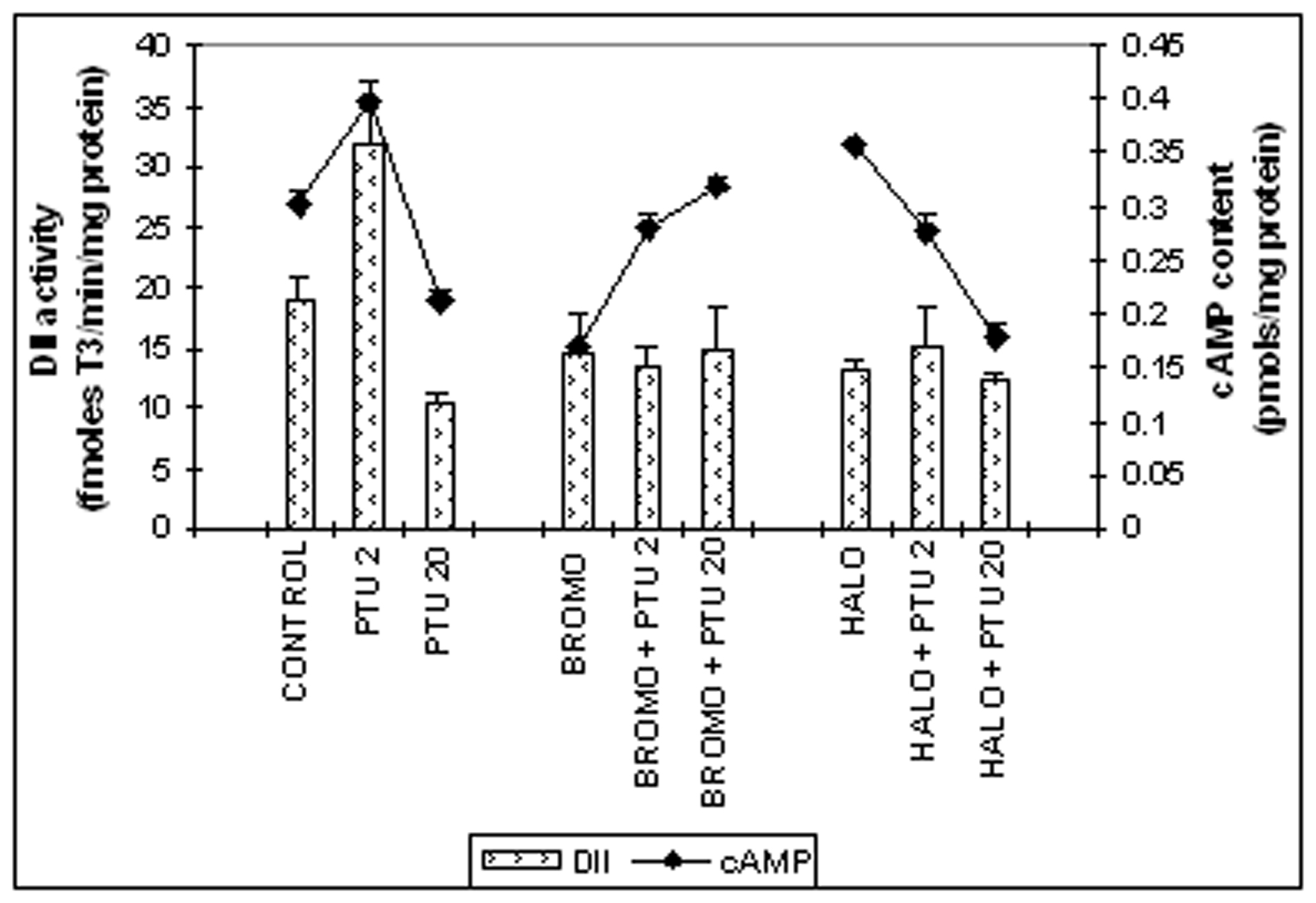
Figure 3. Cerebro-cortical 3, 5, 3'-iodothyronine deiodinase type II (DII) activity (fmoles T3 formed/min/mg protein) and cAMP content (pmoles/mg protein). Daily intra-peritoneal injections of different doses of Bromocriptine (BROMO, dopaminergic agonist) and Haloperidol (HALO, antagonist) were given to adult male Sprague Dawley rats either singly or in combination with PTU (2 mg/100g b.w.) for the first (Day ‘0’ and ‘1’) and last (Day ‘18’ and ‘19’) two consecutive days preceding the onset (Day ‘2’) and termination (Day ‘20’), respectively, of 'central thyroid hormone homeostasis'. Parallel control animals were injected with equal volume of vehicle. Animals were sacrificed and cerebral cortex collected on Day ‘2’ and Day ‘20’ (after 24 h of the last injections) for determination of DII activity. Data are presented as Mean ±SEM of 12 - 15 individual animals in each group, pooled from three sets of experiments. The vertical line denotes standard error.


