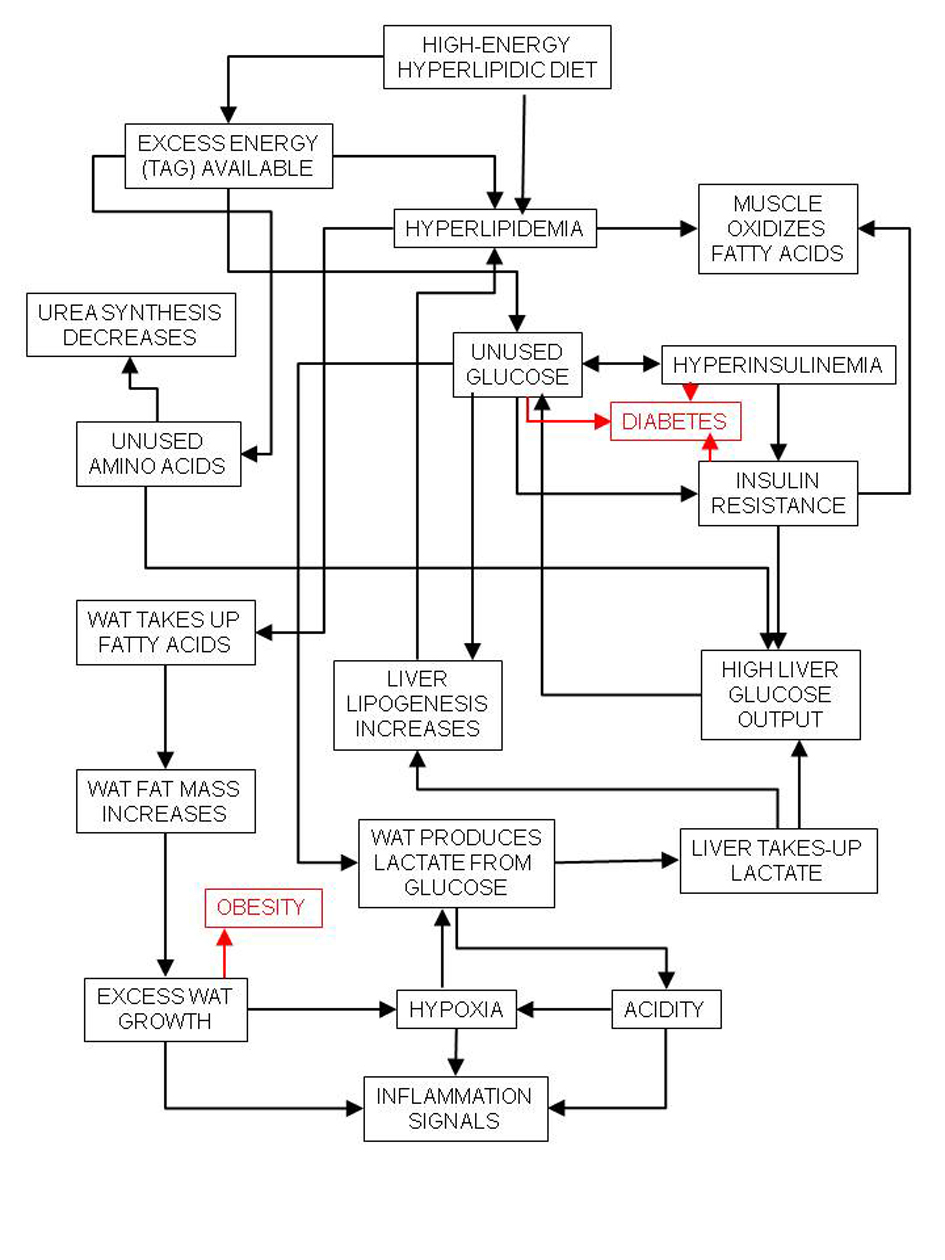
Figure 1. Relationships between high-energy (high-lipid) diet and inflammation and its main consequences, diabetes and obesity.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Review
Volume 2, Number 4-5, October 2012, pages 155-165
Metabolic Syndrome: A Multifaceted Disease of Affluence
Figures

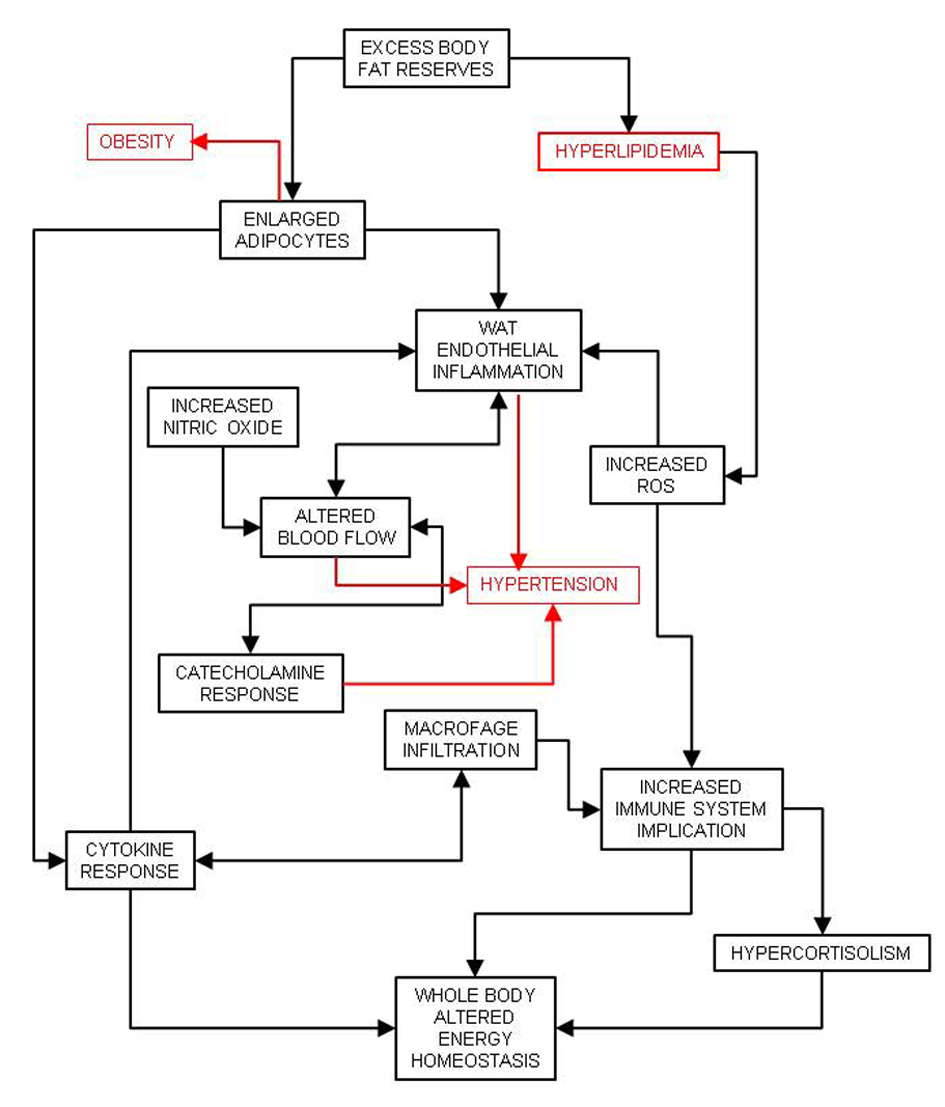
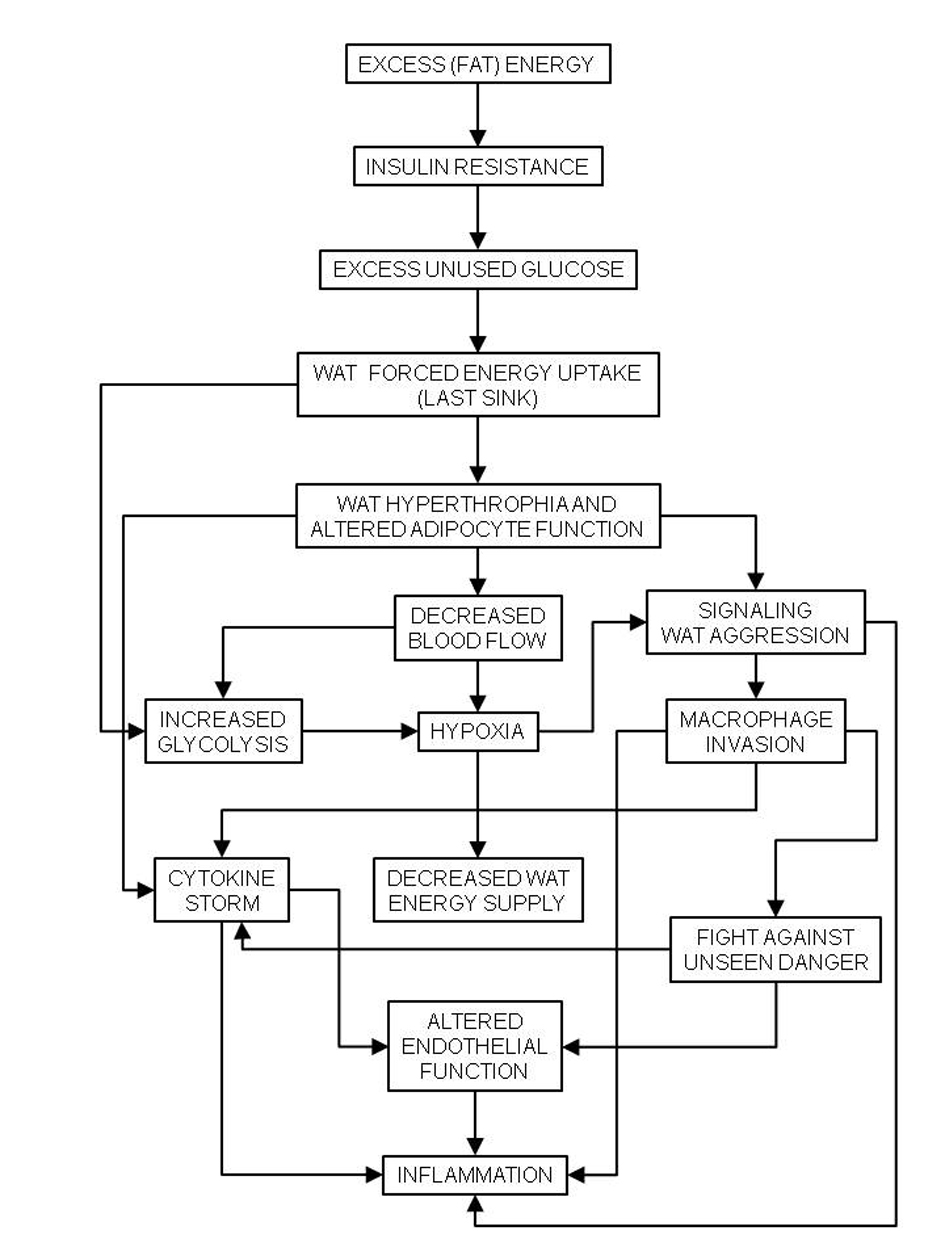
Table
| Insulin resistance | Decreased sensitivity to glucose/Low peripheral tissue glucose uptake/Type 2 diabetes/Dementia/Alzheimer disease |
| Hyperlipidemia/dyslipoproteinemia | Small, dense LDLs/Hypercholesterolemia and low HDL cholesterol/Hypertriacylglycerolemia/High ApoB/Oxidized lipoproteins |
| Hepatic steatosis and hepatomegalia, Altered hepatic function | hyperbilirubinemia/Increased enzyme leakage/Altered antioxidant mechanisms/Altered xenobiotic metabolism |
| Hyperuricemia/gout | Inflammatory arthritis |
| White adipose tissue inflammation | Obesity/visceral or upper body obesity/Adipocyte hyperplasia and proliferation/High proportion of nonadipocyte cells/massive macrophage infiltration/Altered blood flow/Hypoxia/High leptin/leptin resistance/Low adiponectin/High resistin Low interleukin-6/increased adipokine signaling |
| Altered immune response | Asthma, psoriasis/Other autoimmune diseases |
| Increased oxidative damage | Increased effects of free radicals, superoxide, peroxynitrite, etc./Increased synthesis and disposal of NO·/Increased nitrite and nitrate excretion |
| Altered composition of the microbiota | Altered immune system control of the biota/presence of nitrate and nitrite/Increased LPS levels/interaction with the biota |
| Acanthosis nigricans | |
| Sleep apnea | |
| Arterial hypertension | Increased peripheral blood flow resistance/Atherosclerosis/increased vascular microdamage and enhanced plaque formation/Altered rheological behavior of red blood cells/nondeformability of red blood cells |
| Increased cardiovascular risk | Atrial fibrillation/Altered blood coagulation/Pulmonary resistance/respiratory insufficiency/Heart insufficiency/Higher incidence of ictus |
| Altered hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenals axis function | Hypercortisolism/Cushing-like states/Disappearance of daily rhythms/Depression, altered thymic states/Altered gonadotropin secretion, infertility |
| Decreased/altered sex hormone metabolism and function | Polycystic ovary syndrome (?)/Hypoandrogenism/Decreased dehydroepiandrosterone/Decreased estrogen protection |
| Altered nervous system functions | Decreased cognoscitive abilities/Higher incidence of psychiatric alterations/Higher autonomic nervous system activity/Peripheral nerve damage |
| Eating disorders: | Binge eating (obesity type)/Orthorexia, anorexia nervosa (secondary) |
| Increased incidence of some types of cancer | Colon, endometrial, renal cell, gallbladder, and upper digestive tracts carcinomas (largely associated with obesity, diet, and estrogen) |