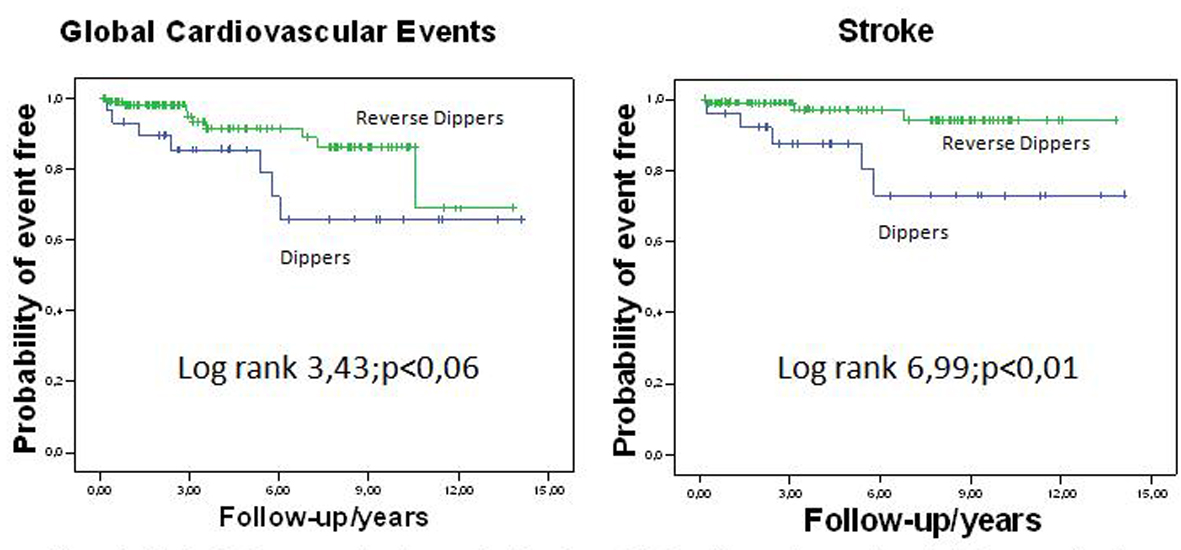
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves showing survival-free from global cardiovascular events and stroke, according to Dipper or Reverse Dipper patterns of nocturnal fall.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Original Article
Volume 3, Number 1-2, April 2013, pages 16-23
Prognostic Value of Low Diastolic 24-H Blood Pressure in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in a Follow-Up of 4.7 Years
Figures

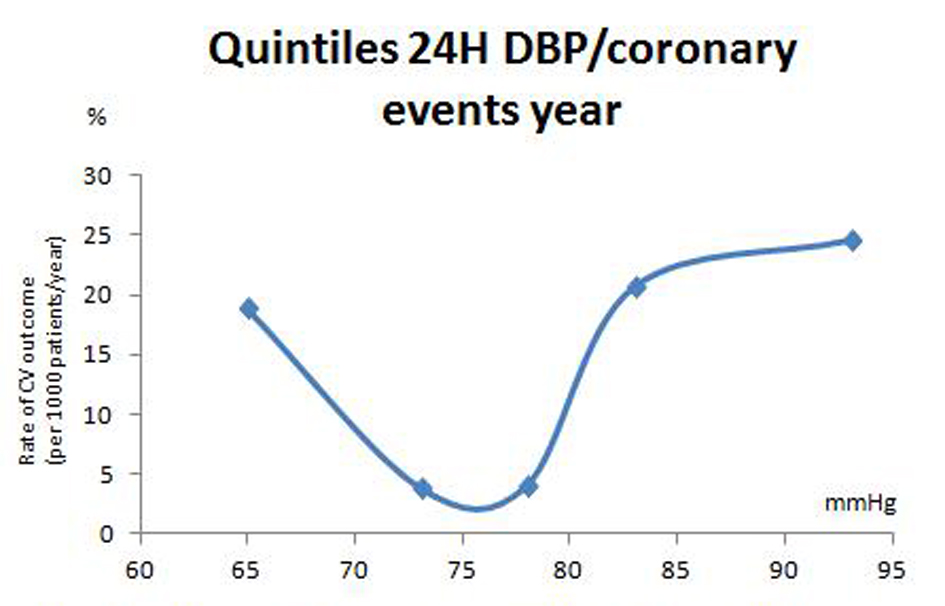
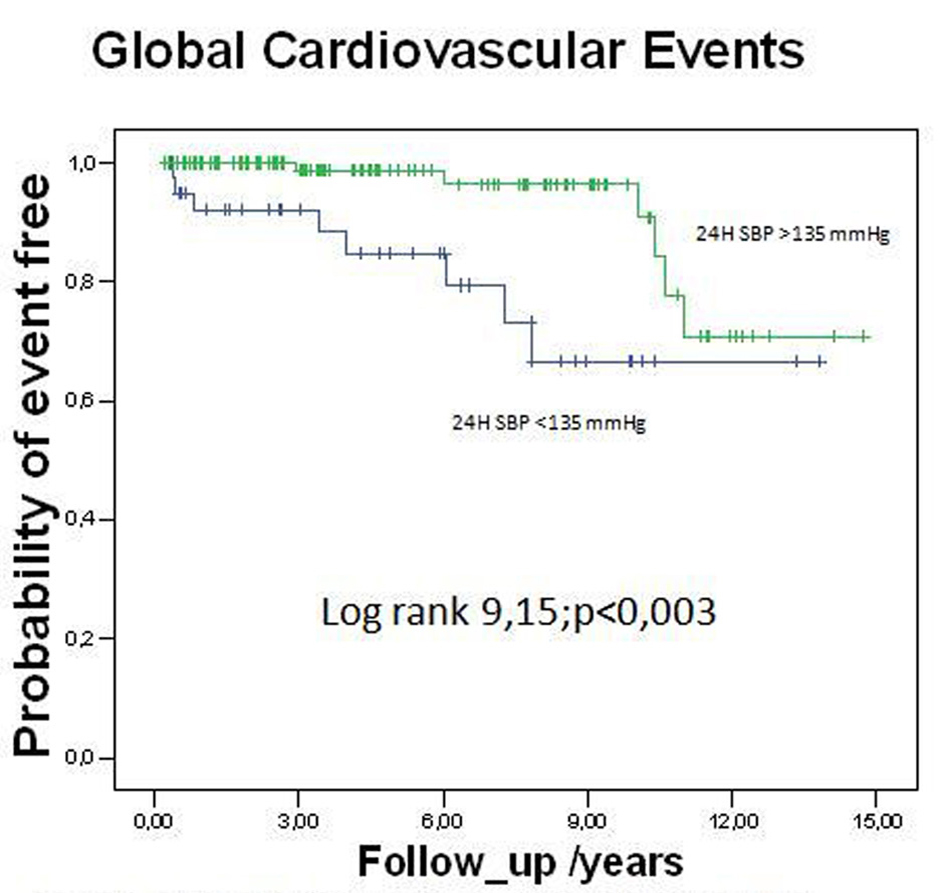
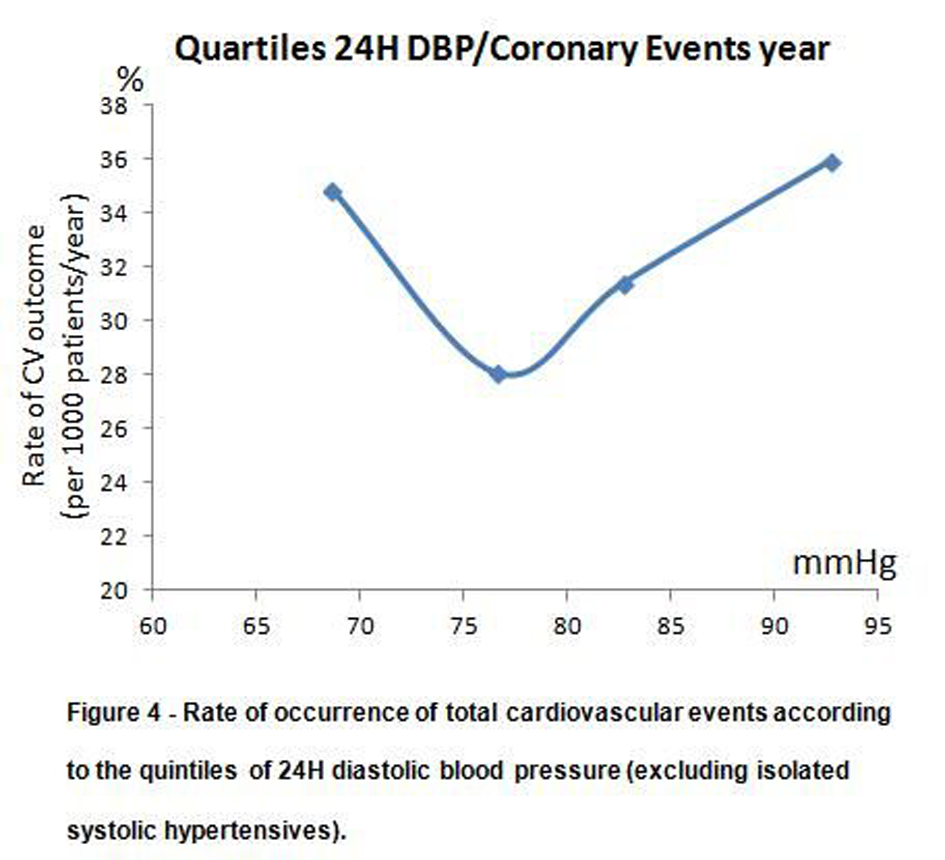
Tables
| Without event (N = 226) | With event (N= 36) | P value | Cardiac event (N =18) | P | Stroke (N = 18) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *: Reverse Dippers vs Dippers; BMI: body mass index; ns: non significant. | |||||||
| Age (years) | 57.9 ± 10.7 | 61.1 ±10.1 | ns | 56.1 ± 9.3 | ns | 66.2 ± 8.4 | 0.001 |
| Gender (male/female) | 110/116 | 21/15 | ns | 14/4 | < 0.02 | 7/11 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.1 ± 4.8 | 30.5 ± 3.5 | ns | 30.3 ± 3.2 | ns | 30. 6 ± 3.8 | ns |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 63.3 | 47.2 | ns | 55.6 | ns | 38.9 | < 0.05 |
| Casual systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 158 ± 24 | 165 ± 32 | ns | 168 ± 27 | ns | 163 ± 37 | ns |
| Casual diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 93 ± 14 | 97 ± 14 | ns | 100 ± 13 | < 0.05 | 94 ± 14 | ns |
| Casual heart rate (bpm) | 81 ± 16 | 80 ± 12 | ns | 83 ± 11 | ns | 78 ± 14 | ns |
| 24H systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 137 ± 15 | 139 ± 15 | ns | 141 ± 16 | ns | 138 ± 14 | ns |
| 24H diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 78 ± 9 | 80 ± 12 | ns | 84 ± 10 | < 0.01 | 77 ± 12 | ns |
| 24H pulse pressure (mmHg) | 59 ± 13 | 59 ± 12 | ns | 57 ± 12 | ns | 61 ± 13 | ns |
| Extreme Dipper/Dipper/Non-Dipper/Reverse Dipper | 12/105*/86/22* | 2/9/16/7 | ns | 1/6/9/2 | ns | 1/3*/7/5* | < 0.05* |
| Medication (%) | 82.7 | 75 | ns | 77.8 | ns | 72.2 | ns |
| ED | D | ND | RD | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED: extreme dipper; D: dipper; ND: non-dipper; RD: reverse dipper; BMI: body mass index; SBP: systolic BP; DBP: diastolic BP; PP: pulse pressure. | |||||
| Gender (male%) | 50 | 54.4 | 49 | 41.4 | ns |
| Age (years) | 61.3 | 56.3 | 59.1 | 61.3 | < 0.05* |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 85.7 | 63.2 | 60.8 | 48.3 | ns |
| Medication (%) | 78.6 | 83.3 | 81.4 | 75.9 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.0 | 30.9 | 29.4 | 28.6 | ns |
| Casual SBP (mmHg) | 167 | 159 | 159 | 150 | ns |
| Casual DBP (mmHg) | 99 | 94 | 93 | 88 | ns |
| 24H SBP (mmHg) | 134 | 134 | 140 | 139 | ns |
| 24H DBP (mmHg) | 75 | 78 | 79 | 78 | ns |
| 24H PP (mmHg) | 59 | 57 | 60 | 61 | ns |