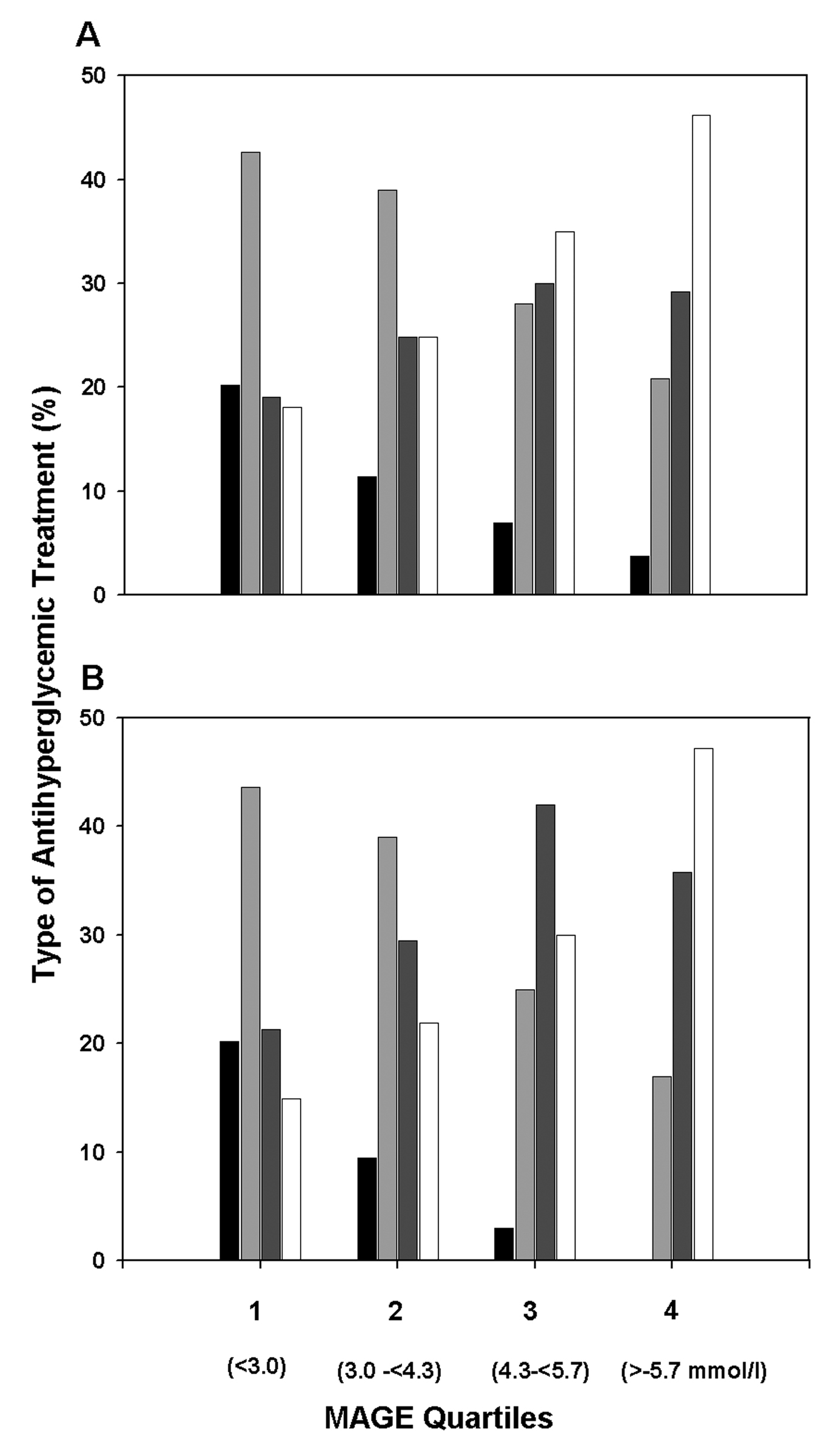
Figure 1. Proportions of various classes of antihyperglycemic medication used for glycemic control in outpatients with type 2 diabetes by quartiles of the baseline mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE). (A) Treatment at baseline. (B) Treatment at 12 month. Indication of treatments: diet (black solid columns), OHA (light grey columns), OHA + insulin (dark grey columns), and insulin alone (white columns). Number of patients in quartiles 1 to 4: n = 94, 105, 100, and 106, respectively.