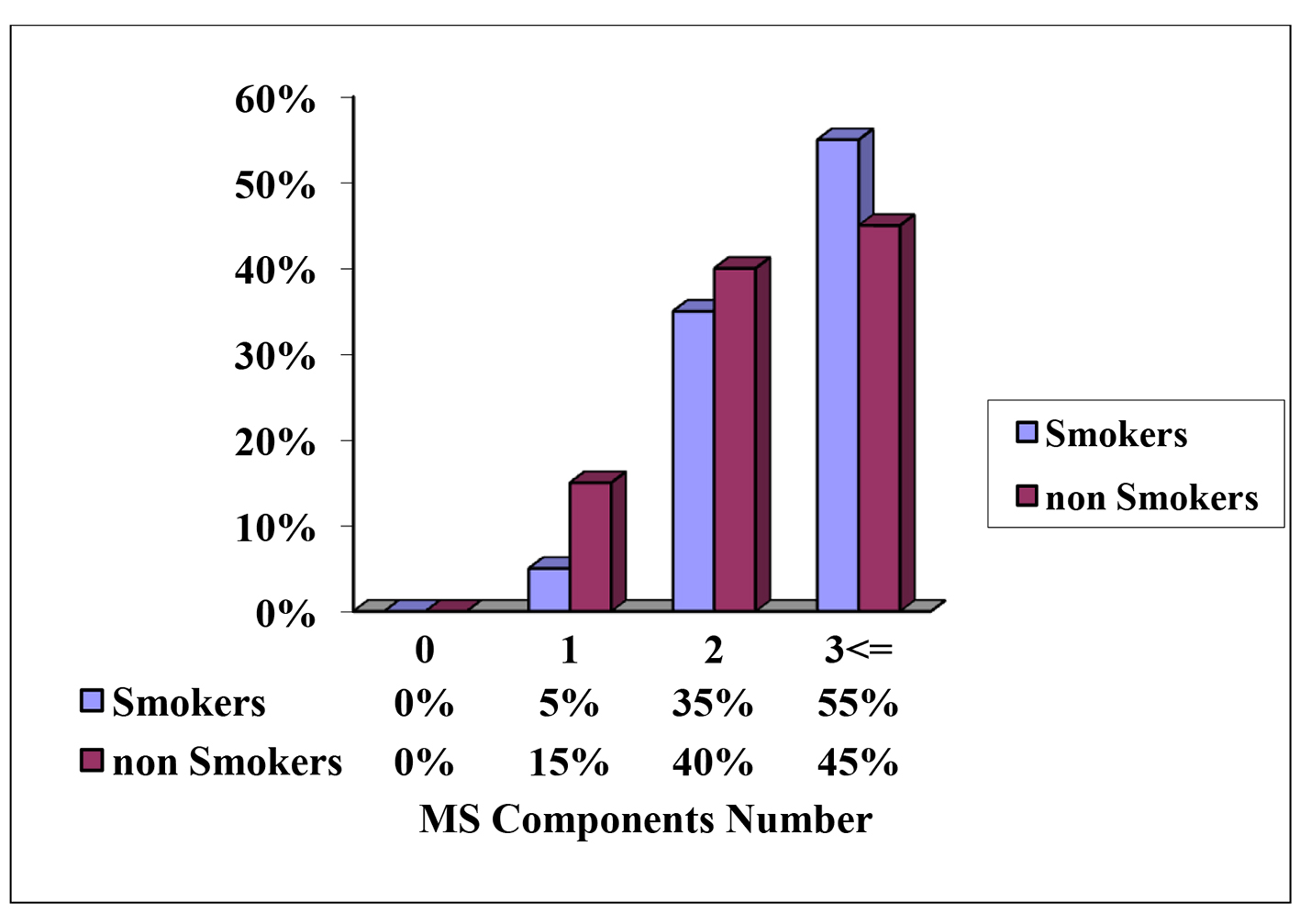
Figure 1. Distribution of the smokers and non-smokers according to the components of metabolic syndrome according to the American Heart Association (AHA) and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) in valid percentage.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 6, December 2016, pages 178-182
Cigarette Smoking as a Relative Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome
Figure

Tables
| Parameter | Group A: smokers (N = 40) | Group B: non-smokers (N = 40) |
|---|---|---|
| Data presented as mean ± SD. *Significance compared to non-smoker, P < 0.05. SBP: systole blood pressure; DBP: diastole blood pressure. | ||
| Age (years) | 53.50 ± 4.19 | 56.85 ± 6.49 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.19 ± 7.15 | 31.76 ± 4.94 |
| Waist (cm) | 105.10 ± 22.99 | 102.15 ± 11.50 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 128.25 ± 13.59* | 120.0 ± 10.00 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 83.25 ± 9.07* | 77.00 ± 9.51 |
| Parameter | Group A: smokers (N = 40) | Group B: non-smokers (N = 40) |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose(mg/dL) | 118.98 ± 20.00 | 134.11 ± 36.56 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 284.72 ± 82.53 | 213.05 ± 61.61 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 115.48 ± 70.19 | 112.23 ± 70.35 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 79.09 ± 65.96 | 60.39 ± 53.11 |
| Triglyceride (TG) (mg/dL) | 270.68 ± 112.68* | 202.15 ± 77.93 |
| Risk factor | Group A: smokers (N = 40) | Group B: non-smokers (N = 40) |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking | 1.22 | - |
| Obesity | 1.44 | 4.31 |
| Dyslipidemia | 2.5 | 1.42 |
| Hypertension | 1.75 | 0.45 |