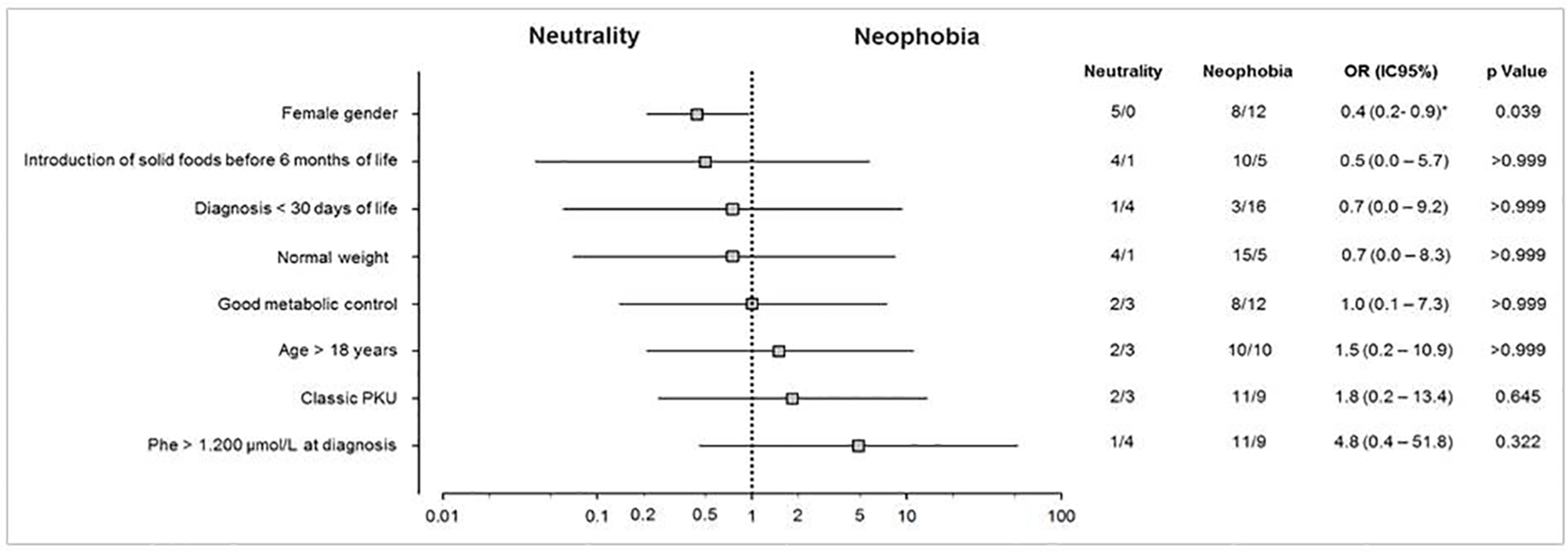
Figure 1. Potential factors associated with food neophobia in patients with PKU. Univariate analysis representing the association between patients with PKU and the factors involved with food neophobia. Odds ratios are represented by a log scale with their respective confidence intervals (95%) and statistical significance (P) obtained by Fisher’s exact test. *Values estimated by the likelihood ratio with Agresti correction. PKU: phenylketonuria.