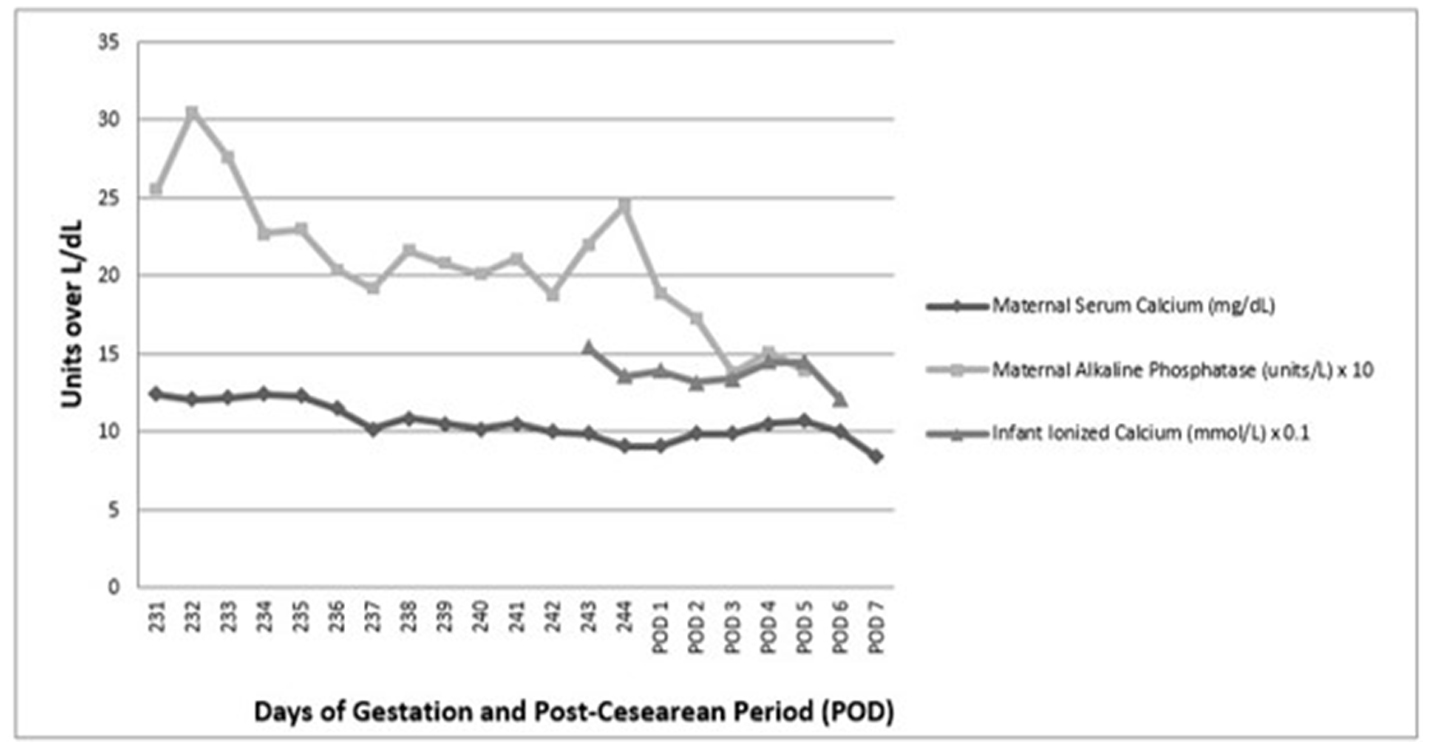
Figure 1. Trend of mother’s calcium, alkaline phosphatase, and neonate’s ionized calcium. Adapted from patient chart through electronic medical record.
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, ISSN 1923-2861 print, 1923-287X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Endocrinol Metab and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jofem.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 2, April 2020, pages 49-53
Medical Management of Primary Hyperparathyroidism in Pregnancy: A Case Report and Brief Literature Review
Figure

Tables
| Initial maternal laboratory data at 32 weeks | |
|---|---|
| Corrected serum calcium (8.7 - 10.2 mg/dL) | 12.6 mg/dL |
| Ionized calcium (1.15 - 1.29 mmol/L) | 1.49 mmol/L |
| Parathyroid hormone level (15 - 65 pg/mL) | 135 pg/mL |
| Parathyroid-related hormone level (0 - 3.4 pmol/L) | 3 pmol/L |
| Vitamin 1,25 level (19 - 79 pg/mL) | 103 pg/mL |
| Alkaline phosphotase level (38 - 126 U/L) | 255 U/L |
| Initial infant laboratory data (post-natal) | |
|---|---|
| Corrected serum calcium (7.6 - 10.4 mg/dL) | 9.8 mg/dL |
| Ionized calcium (1.15 - 1.29 mmol/L) | 1.54 mmol/L |