IMPORTANT! |
|
|
-
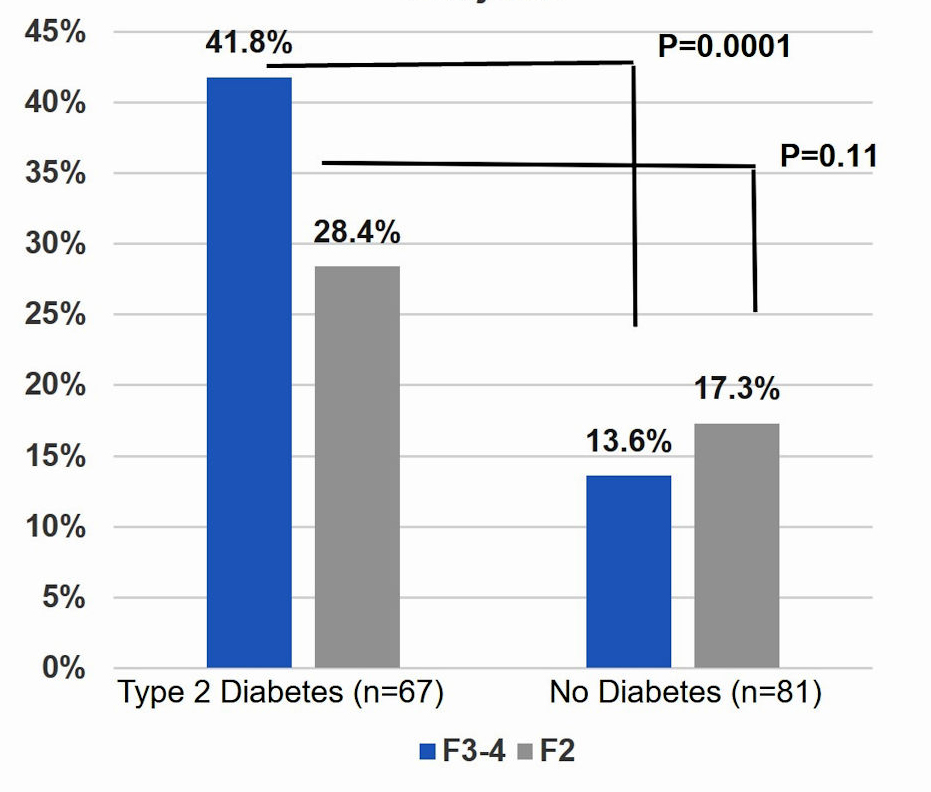
 Associations Between Type 2 Diabetes Subtypes and Complications: Analysis of the Malaysia National Diabetes Registry
Associations Between Type 2 Diabetes Subtypes and Complications: Analysis of the Malaysia National Diabetes RegistryThe aim of the study was to investigate type 2 diabetes (DM2) subtypes and associations with complications in a multiethnic Asian population. DM2 subtypes associate differently with complications in Malaysia, similar to patterns found in European cohorts.
Read More >> -
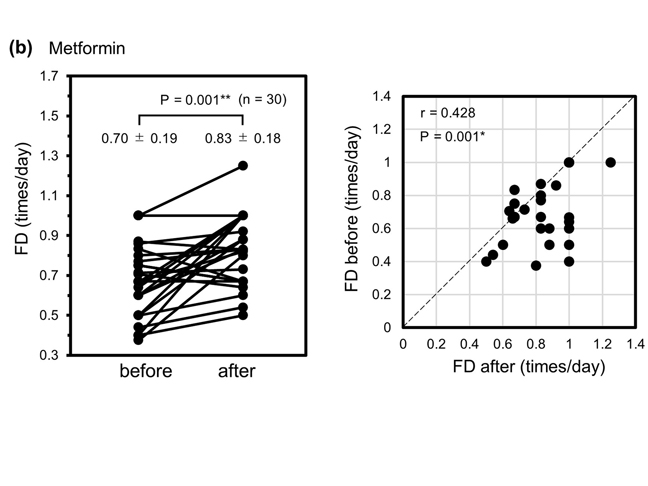 Improvement of Glycemic Control by Metformin Is Associated With Frequency of Defecation Before Treatment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Improvement of Glycemic Control by Metformin Is Associated With Frequency of Defecation Before Treatment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusIt was recently reported that metformin induces glucose excretion in the terminal ileum. This study reassessed the ability of metformin to promote defecation and its relationship with the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Read More >> -
 Thyroid Gland Dysfunction and COVID-19 Severity: Is There a Correlation?
Thyroid Gland Dysfunction and COVID-19 Severity: Is There a Correlation?It has been suggested that thyroid gland dysfunction in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients can directly or indirectly affect COVID-19 severity and mortality rates.
Read More >> -
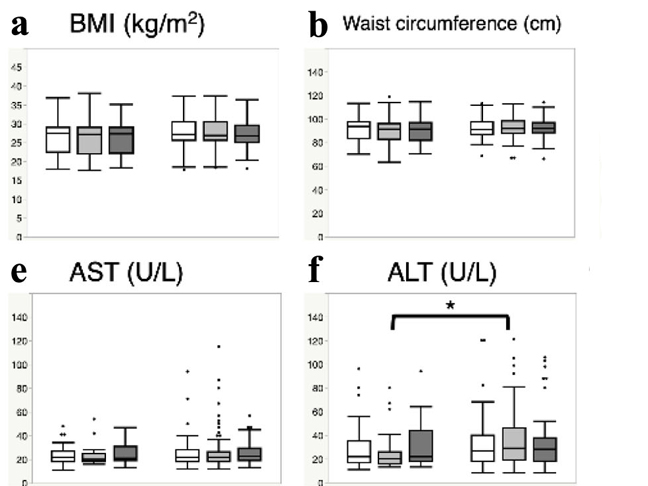 Application of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Lifestyle Improvement After Health Checkup
Application of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Lifestyle Improvement After Health CheckupAlthough workers are required to undergo annual health examinations in Japan, many issues remain with encouraging examinees to visit medical institutions after the checkup and providing education in lifestyle improvements.
Read More >> -
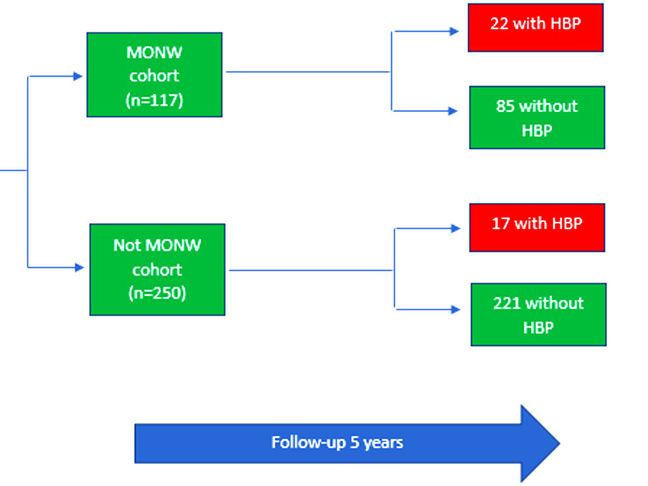 Metabolically Obese Normal-Weight Phenotype as a Risk Factor for High Blood Pressure: A Five-Year Cohort
Metabolically Obese Normal-Weight Phenotype as a Risk Factor for High Blood Pressure: A Five-Year CohortThe metabolically obese normal-weight (MONW) phenotype has been considered a risk factor for different chronic diseases, but its role in high blood pressure (HBP) is still unclear. The aim of the study is to determine if the MONW phenotype constitutes a risk factor for hypertension in Peruvian adults belonging to a 5-year cohort.
Read More >>
Featured | Featured | |||
| The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a weekly monitoring interaction using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in a population of poorly controlled type 2 diabetes patients. Full Text | |||
Key Clinical Image |
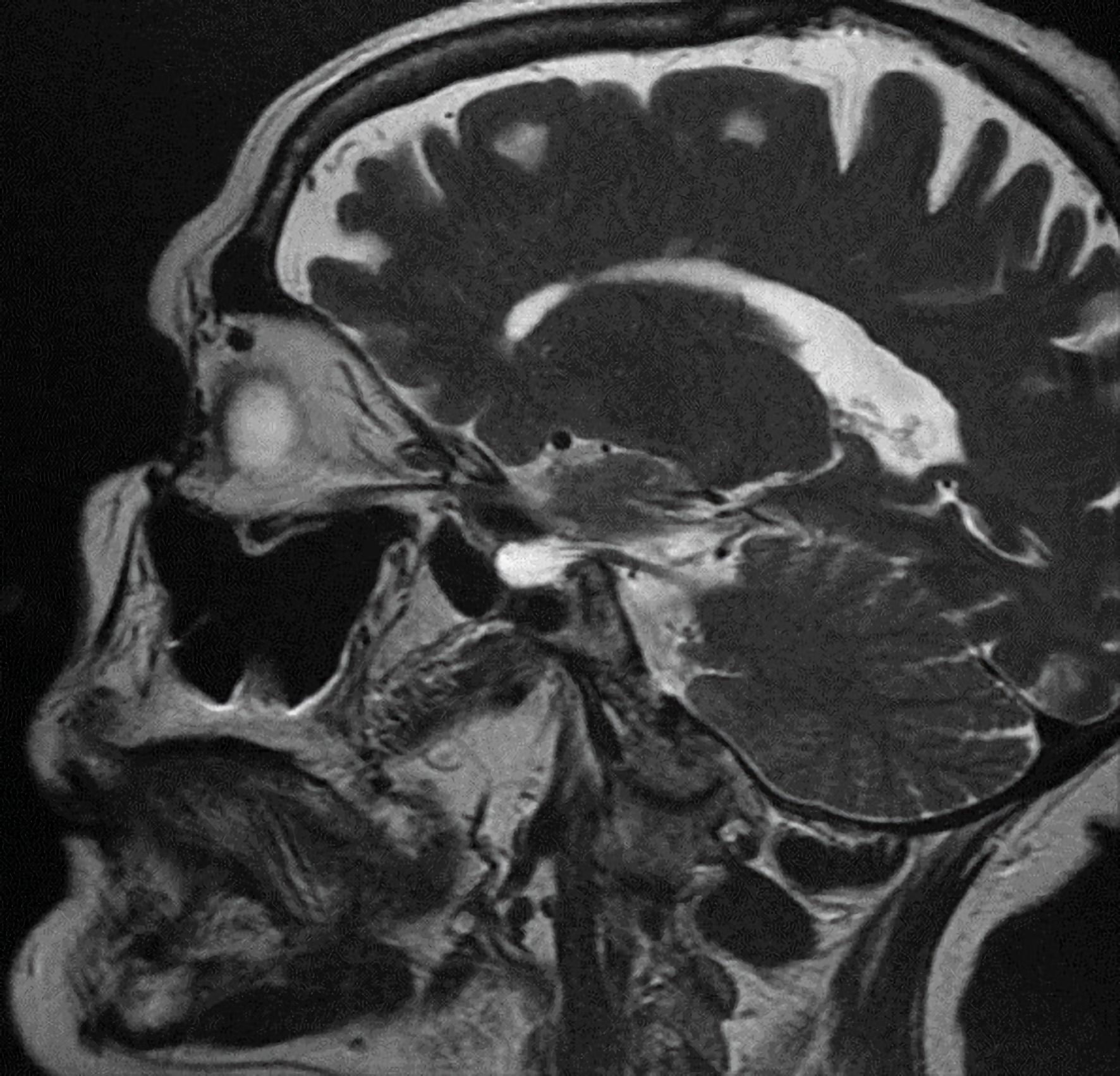 Sheehan Syndrome in a Fifty-Six-Year-Old Woman Presenting With a Retroperitoneal Mass: Perioperative Management During a Major Surgery |